Short Message Service (SMS) and how does it work?
What is SMS?

SMS stands for Short Message Service, as the name states it consists of an exchange between mobile devices as short as 160 characters plain text message using protocols that are shared across all those platforms.
It is commonly known as texting, it sends text-only messages being one of the oldest texting technologies and most frequently used.
The best part of using this is that unlike other apps it doesn’t need to be downloaded or even updated. It’s available to everyone with the know-how to use it.
First SMS appeared in Europe on 3rd Dec 1992 when Neil Papworth a test engineer for Sema group. He used a PC to send “Merry Christmas” to the phone of colleague Richard Jarvis.
After that, it was included in the GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) standards right. But then after some time, it was ported to wireless technologies like CDMA and TDMA.
3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project) was responsible for the maintenance of both GSM and SMS, now it is ETSI (European telecommunication standards institute).
Advantages of SMS
The number of SMS texts exchanged every day is huge, the reason which leads to the success of SMS are:
- Even if the recipient’s phone is switched off it can be sent, and will be delivered as soon as the mobile gets on again.
- it is supported by 100% GSM mobile phones, and this is considered the biggest advantage.
- SMS messages can be sent and read at any time
- It is faster and easier to use, the most convenient one.

Now, let us see some examples of SMS applications to give you some more clarity about what more can be done with SMS messaging.
- P2P:
It is typical human-to-human communication, where a person sends a message to another person. When the recipient’s mobile phone receives the SMS text message, it will notify the user by giving out a sound or vibrating. The user can read the text message sometime later or immediately and can send a text message back if he/she wants. - A2P:
It is an Application to Person SMS, generally used for business purposes. They use text messages to send information such as news, weather report, and financial data to their subscribers. Many of these services are not free and the users are charged a certain fee, the fee will either be included in the monthly mobile phone bill or be deducted from prepaid card credits. - Alert and Notification:
SMS is a very suitable technology for delivering alerts and notifications of important events, such as E-commerce, credit card transactions, stock market alerts, etc. - SMS Marketing:
It is same as an advertising channel that allows businesses to advertise, promote, and engage with their audience through text messaging. The benefits of text message marketing over traditional forms of marketing are that texts are a personal way of communication, and SMS messages have a 98% open rate.
When you are using a web or some other application on your PC to send the bulk SMS for promotional or transactional you need an interface that allows sending SMS without using a mobile phone and that is an SMS gateway.
How does SMS work?
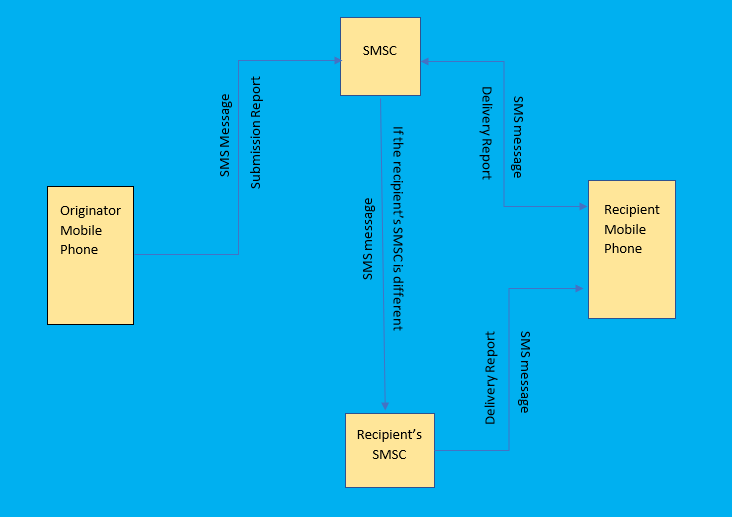
It starts when you press “send” on your SMS, your message is interpreted into data and sent across a detailed web of interconnected carrier networks that is SMSC. Your message will search for the fast path to the designated recipient. Once found, the data is interpreted back into a message and is delivered to the device by SMSC.
If both you and recipient are using the mobile phone service of the same wireless network operator, then the transmission of SMS message involve only one SMSC. This SMS message is called an intra-operator SMS message.
When you and recipient are using the mobile phone service of wireless network operator A an wireless network operator B respectively, then the transmission of SMS message involves two SMSC. This SMS message is called an inter-operator SMS message.
What is SMSC?
SMSC (SMS center) is responsible for handling all the SMS operations like receiving, storing, routing, and forwarding, Its primary job is forwarding messages to recipients and storing SMS messages if the recipient isn’t immediately available now let’s see how this work…
SMSC is typically involved in the transmission of messages during the communication between mobile phones.
And if the recipient is not in the same network so first SMSC forward it to the correct SMSCs. Then SMSC checks whether the recipient is available or not, if not then it stores, and as soon as the recipient is available it will forward it to the recipient’s mobile.
The SMSC works with the other components of a mobile network to determine if the recipient is online. This includes the home location register (HLR), the visitor location register (VLR), and the mobile switching center (MSC).
How does those component work with SMSC?
To know where a terminal is at any time, the network must be able to track it while it is moving. For this purpose, signaling messages need to be frequently sent to update the network’s information about the user’s location. In particular, the system is divided into location areas, and every time the user crosses the boundary of one of those, a location update message is sent.
Lets understand them one by one.
Home location register (HLR):
The Home Location Register (HLR) is the main database in a wireless network containing customer data, including service entitlements and call-routing information of permanent subscriber information for a mobile network.
Visitor location register (VLR):
VLR contains information regarding users who are registered as subscribers somewhere else but happen to be roaming in the area.
Mobile switching center (MSC):
The network is divided into service areas, each composed of several cells managed by a central unit, that central unit is Mobile Switching Center. it performs as a host of routing SMS messages, conference calls, fax, and service billing as well as interfacing with other networks.
Every time a user registers as a roamer in a new area, some signaling takes place between the MSCs involved, and the databases are appropriately updated. The information contained in those registers allows the network to locate the user, i.e., to identify the set of cells where the user can be found at any given time.
Wrapping Up
Ultimately, SMS is an amazing tool for many purposes, let it be texting your friend, getting alert messages of bank statements, or marketing all can be done… and getting the details about how it works helps us to use it more widely and conveniently.

What an awesome post, I just read it from start to end your blog post, An informative blog.
I learned that your articles’ contents and writing abilities are both consistently excellent. Thank you for providing this article; it contains information that is extremely important to me. so thankyu so much for a lovely content.
Boss83